Tunisia Economic Resilience & Inclusion (TERI)
Supported Work
TERI Anchor Trust Fund
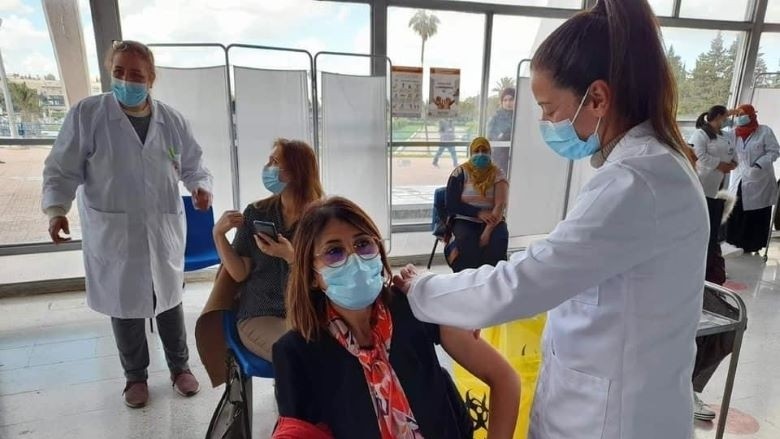
Health
The difficulty to access vaccines in the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated the importance of investing in local vaccine production capacity. Responding to this challenge, TERI has swiftly mobilized resources to provide technical assistance to the Government of Tunisia for the elaboration of a national vaccine production strategy. The objective of this technical assistance is to support the elaboration of a national strategy and roadmap for Tunisia to produce priority vaccines, become self-sufficient, and export excess vaccines. This assistance further supports the government’s efforts in securing investments for vaccine production, which aligns with the country’s recent designation by the World Health Organization (WHO) as one of the six mRNA technology transfer hubs.
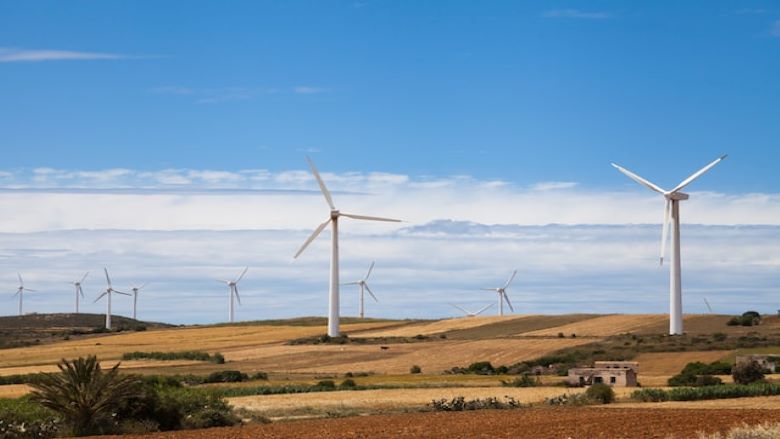

Energy
Developing a strong national energy sector takes a combination of institutional and private-sector knowhow and expertise. To support the Government of Tunisia in its efforts to improve the performance and financial viability of the energy sector, and more specifically the renewable energy sector, the TERI Umbrella provides technical assistance through two distinct components: (i) determining the methodology and framework for billing excess energy from self-producers to the public utility grid for energy self-generation schemes; and (ii) identifying and addressing the barriers to financing renewable energy projects, with a strong focus on local banks under the authorization scheme. These two activities work towards setting the base for a performing and accessible renewable energy sector in Tunisia, which constitutes one of the country’s key future growth-enabling industries.

Social Protection
In a context where the Government of Tunisia is committed to alleviating multidimensional vulnerability and poverty through social protection systems and services, the TERI Umbrella Program is delivering technical assistance to strengthen national social safety nets for the poorest and most vulnerable populations in Tunisia. In close collaboration with UNDP, the World Bank is currently conducting the inception phase of a three-year project which intends to improve access to both legal aid mechanisms as well as integrated and people-centered social protection delivery systems to strengthen the resilience of most vulnerable populations. The project will provide support to the Amen national social assistance program, which serves over a million individuals in Tunisia.
Moussanada Associated Trust Fund

Governance Window
This technical assistance program is part of a broader national initiative to reform the civil service and promote the modernization of the administration. This technical assistance program is structured around three components: (i) the modernization of human resources management; (ii) administrative simplification and improved access of citizens to public services; and (iii) digital governance. The project has contributed over the past years to improve human resource management and mobility/redeployment to needed functions and regions, through the official launch and public opening of the first Job Mobility e-Platform in Tunisia in April 2021. Since, 517 civil servants have applied for mobility.

Better Jobs Program
The persistent mismatch between the demand and supply of skills in the domestic labor market is one of the reasons behind the high youth unemployment rate in Tunisia. This project aims at increasing the outreach and quality of intermediation and orientation services proposed to job seekers, collaborating closely with private and public sector stakeholders. The proposed technical assistance is part of the broader EU4Youth program, which supports the modernization of the ‘Agence Nationale pour l’Emploi et le Travail Independant’ (ANETI) by revamping its services to fully meet the needs of job seekers and enterprises, whilst also digitizing its tools and processes. Recent results include the possibility of registering online, updated modules on job search techniques for job seekers, and the conception of new job seeker segmentation methods for counselors to provide more tailored services.

Financial Sector Window
Strengthening the resilience of Tunisia’s economy to shocks for a more inclusive and durable growth accessible to all citizens is critical to address the growing impact of climate change. This technical assistance program aims to promote greater levels of financial stability through insurance markets and financial resilience mechanisms, articulated around three components: (i) insurance markets; (ii) national disaster risk financing and associated insurances; and (iii) banking. Implemented activities vary from assessing current practices and organizing capacity-building workshops to supporting the drafting of new regulations and operational manuals.

Regionalization and Decentralization Window
Strengthening the capacities of national counterparts to play a more prominent role in the decentralization process is a key activity area of the Moussanada Trust Fund in Tunisia. Through various competency-based trainings, the project is strengthening the capacities of magistrates of the Tunisian Court of Account to enable the subsequent operationalization of the updated Local Government Audit Manual. The technical assistance provided is helping the magistrates to sharpen their investigative techniques and acquire the necessary communications expertise to bolster their public speaking and better communicate their role in the decentralization process. The project has also enabled the creation of a platform centralizing audit reports, helping to fight against fraud and corruption at a more local level.
TRACE Associated Trust Fund

Supporting the Economic Recovery and Job Creation in the Agri-Food Sector
This project provides grants to producer organizations, SMEs, and young entrepreneurs working in agribusiness to improve their resilience and competitiveness, helping them to develop their businesses and create additional jobs in the agricultural sector. The project is being carried out by three implementing partners in the governorates of Gabes, Jendouba, and Kairouan. These grants are flexible and can be used to finance the different inputs, equipment, services, and training needed for these organizations to grow their businesses and create jobs in their regions. At the same time, the project provides technical assistance, alongside with grants, to support beneficiaries in designing and then implementing their business plans. The project targets a large variety of businesses working in agriculture, from farm production and processing to agri-service providers and agrotourism.

Supporting Youth Employment in Rural Areas
Agriboost promotes employability for youth in the rural agricultural sector. Agriboost will provide training sessions to young job seekers so that they can find a wage job in an existing agri-firm or start their own business in agriculture. This project is a collaboration with three government agencies involved in job creation and agriculture, supporting the modernization of their employment support programs. In its initial pilot phase, Agriboost will support 200 young applicants in the governorate of Kairouan.

Nexus Skills & Jobs for Youth and Women
The objective of the NEXUS skills & jobs project is to address the skills mismatch between supply and demand in the agri-food sector by developing, testing, and anchoring methodologies and tools that bridge the gap between the qualifications and competencies needed by employers and those offered by Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) institutions in the agri-food sector. NEXUS will contribute to a better understanding of the private sector needs , particularly in the agri-food industry, by identifying skill gaps, updating job qualification frameworks, adapting the education and vocational training system to the identified needs, and training youth.
Compact with Africa Associated Trust Fund ( This fund has closed on 31.12.2023 )

Project Development Fund for Public-Private Partnerships
In December 2021, the Government of Tunisia launched a project development facility (PDF) to accelerate the development of a pipeline of public-private partnerships (PPP) projects in the country. Created as a special fund under national law, the structuring and preparation of the mechanism greatly benefited from the World Bank’s technical assistance. In close collaboration with Tunisia's National PPP Unit (IGPPP), the World Bank is helped design the fund's governance, business plan, and operating procedures. The PDF was set to operate for five years, and it was forecasted to support the government in delivering an ambitious PPP program of more than US$4.5 billion in investments targeting strategic sectors such as renewable energies, sustainable transport, water desalination, and wastewater treatment.

Developing Partnerships for Entrepreneurship
Partnerships for entrepreneurship (PPEs) aimed to foster innovative forms of private-sector initiatives and public-private collaborations to strengthen the delivery of basic services at the local level. This project enabled municipalities, or government entities providing local services, to crowd-in private sector initiative through the design and launch of a project accelerator. The setting up of this mechanism intended to support entrepreneurs to develop and submit proposals of impactful projects and complemented existing work on strengthening the PPP framework in Tunisia. Successful delivery of pilot programs will served as examples and promoted the scale-up and/or emergence of innovative public-private projects, diffusing a culture of quality management in the local administration.

Strengthening Capacities and Knowhow in Value Chain Financing
The World Bank supported the Tunisian Central Bank (CBT) in improving its understanding of value chains, collection and management of credit and financial data, risk supervision capability, as well as policy formulation and advocacy capability in relation to value chains. In Tunisia, two pilot value chains in cereal and olive oil production were chosen, as they offered significantly positive prospects with regards respectively to better food security and higher revenue in agriculture. These two value chains were selected jointly with the CBT for the size of their employment capacity, contrasting financing modes, and impact on foreign exchange generation and the national budget.
