Results
Mauritania’s advantageous geographic location between Sub-Saharan Africa and the Maghreb means that it has enormous regional economic potential. The activities delivered under the WARCIP have already led to enormous improvements in the digital landscape in Mauritania, thereby allowing the country to cultivate the benefits of ICT for economic growth, job creation and regional integration. The results can be traced back to the beginning of quarter (Q)1 of 2021, which is when parts of the fiber optic backbone became operational.
- The project also made contributions through technical assistance efforts to strengthen the governance of the telecommunications sector, specifically by helping to develop the legal and regulatory framework. It facilitated the preparation of strategic studies to promote broadband and universal access. It also supported the regulation of licensing, as well as infrastructure sharing and capacity building for key institutions.
- The project allowed Mauritania to promote private sector participation in economic activities, helping it to foster investments from telecommunications operators and Internet service providers through participative institutional arrangements (namely, PPPs).
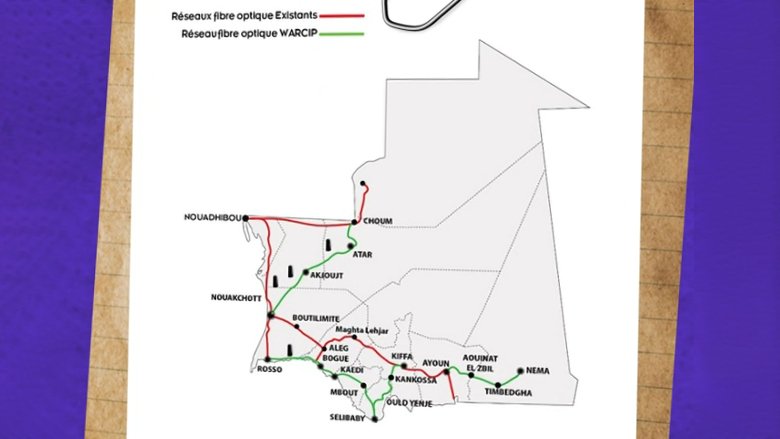
- The project has contributed to extending connectivity to previously underserved or unserved areas through the deployment of 1,700 km of strategic fiber optic links. The first link of 531 km connected the cities of Atar, Choum, and Nouakchott. The second link of 723 km connected the cities of Boghé, Kaédi, Kiffa, Rosso and Selibaby. The third link of 280 km connected Aioum to Nema. The fourth link of 43 km connected Selibaby to the border with Mali. Finally, a fiber optic loop link in the capital, Nouakchott, provided the necessary backhaul capabilities to efficiently distribute the international capacity from the newly deployed ACE cable connection. In addition, it allowed the telecommunications operators in Mauritania to extend the 4G mobile broadband throughout the territory that had otherwise been limited in terms of mobile connectivity. As a result, this milestone will promote the development of productive cities, allow all parts of the country to contribute to economic activity, as well as generate additional revenues. Indeed, the total revenues of the deployed backbone for 2021 and Q1 of 2022 amounted to US$2,132,935.
- The new digital infrastructure contributed to reducing the cost of connectivity by: (i) allowing for a more affordable international connectivity through the ACE submarine cable connection to reach other areas of Mauritania through an open access backbone; (ii) improving national traffic through higher bandwidth capacity of the deployed fiber optic links; and (iii) improving the routing of national Internet traffic, thereby reducing the cost of Internet Protocol (IP) transit through the deployment of an Internet Exchange Point (IXP). These benefits translate into more affordable retail prices for communication services to end users. As such, they also help to drive the increased adoption of digital technologies.
The project established an environment conducive to digital transformation in Mauritania by supporting the legal and regulatory framework, as well as the deployment of broadband infrastructure that is essential to the country’s socioeconomic transformation, innovation, and job creation, particularly for women and youth. Broadband became more available, accessible, and affordable thanks to the activities financed by the WARCIP. For example, the average monthly price of wholesale broadband access decreased from US$7,000 a month at the beginning of the project to US$54.70 at project closure, as compared to a target of US$250 (for 2 megabits [Mbit/s]) — far exceeding all expectations. Access to broadband Internet services increased greatly from a baseline of 2 percent to 71 percent, again far exceeding the expected target of 11 percent. In addition, the number of localities connected to broadband has increased significantly from 144 to 221, as compared to a target of 200. These improvements also resulted in better opportunities for the Mauritanian population, positively impacting university networks, incubation hubs, and startups, thereby promising a substantial increase in available, higher quality job opportunities, as well as increased adoption of digital financial services, such as mobile money platforms and mobile banking.