What is ETRI?
As a result of a close collaboration between the World Bank’s Education Global Practice and Imaginable Futures, the Education and Technology Readiness Index (ETRI) - a multi-dimensional easy to use and free of cost global instrument- was designed and has been tested simultaneously in three different continents to support countries in assessing where they stand on education technologies. Although it is not a full diagnostic tool, ETRI identifies and measures the different enabling factors that are required for EdTech to be effective (e.g., mindset, buy-in, budget, technical infrastructure, and human and technical capacity), which can help governments pinpoint where there is room for improvement, and signal to countries their overall level of readiness to deploy effective EdTech policies.
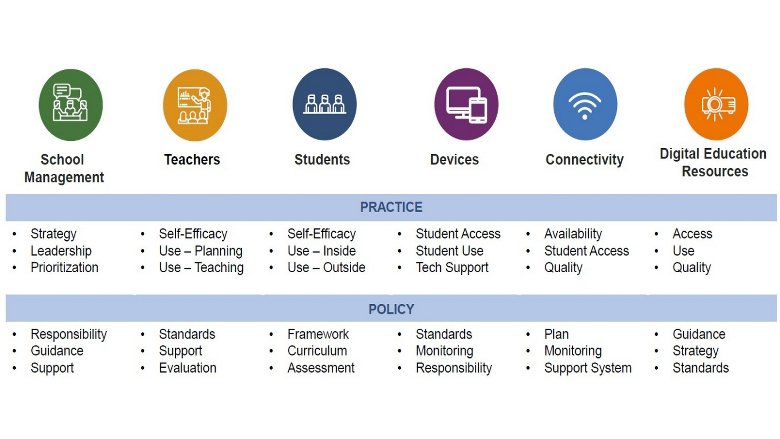
What are the key components of ETRI?
The ETRI framework is organized around the EdTech practices (or service delivery) and policies that could impact a country’s quality of education services and resulting learning outcomes. The practices (activities and conditions associated with the use of digital technologies in school) and policies (how the system defines, articulates and implements strategies to foster the desired practices) are two of the three dimensions of the World Bank’s Global Education Policy Dashboard (GEPD). The practice and policy dimensions are broken down across ETRI's 6 overarching pillars, which are believed to play a role in the education ecosystem: School Management, Teachers, Students, Devices, Connectivity, and Digital Education Resources.