Key Achievements:
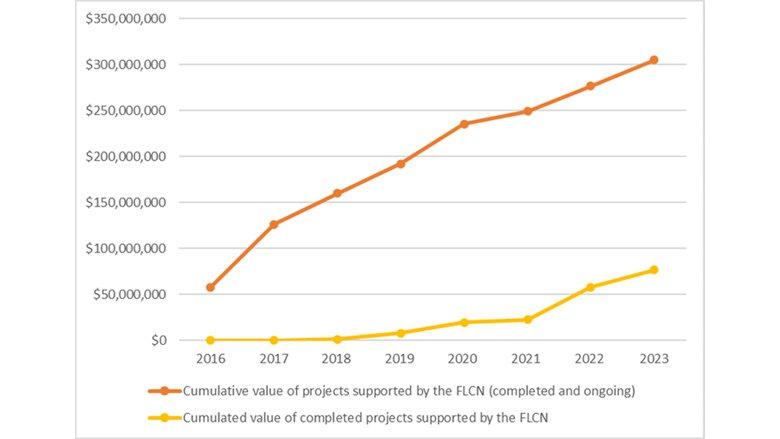
- Risk reduction: Financing and implementation of more than 230 disaster risk reduction projects, worth $304 million. Completed disaster risk reduction projects, amounting to $76.6 million, have benefited around 400,000 direct beneficiaries and over 33 million indirect beneficiaries across the country.
- Institutional strengthening: Creation and operationalization of a new Directorate for Disaster Risk Management and adoption of Morocco’s first National Disaster Risk Management (DRM) Strategy (2021–2030).
- Financial protection: Implementation of an innovative public-private disaster risk financing (DRF) regime, providing coverage to the entire Moroccan population through private insurance and a public Solidarity Fund. Unlocking of $300 million after the 2023 Al-Haouz earthquake.
- Disaster preparedness: Flood risk early warning system operational in four pilot provinces, directly benefiting an estimated 240,000 people.
- Risk understanding: Improved understanding of disaster risks through multi-hazard risk assessment at the national level, and two urban resilience diagnostics and strategies developed at the local level.
Challenge:
Morocco is among the countries most exposed to geological and climate-related hazards in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. In particular, it is highly vulnerable to earthquakes, floods, landslides, and droughts. The Al-Haouz earthquake of September 2023 exemplifies the severity of these risks: it affected at least 300,000 people, destroyed 60,000 buildings, and killed nearly 3,000 people. The World Bank estimates that disasters cost Morocco over $575 million per year. Urbanization and climate change are expected to further exacerbate disaster risks in Morocco, including through an increase in the frequency and severity of hydrometeorological hazards.
Approach:
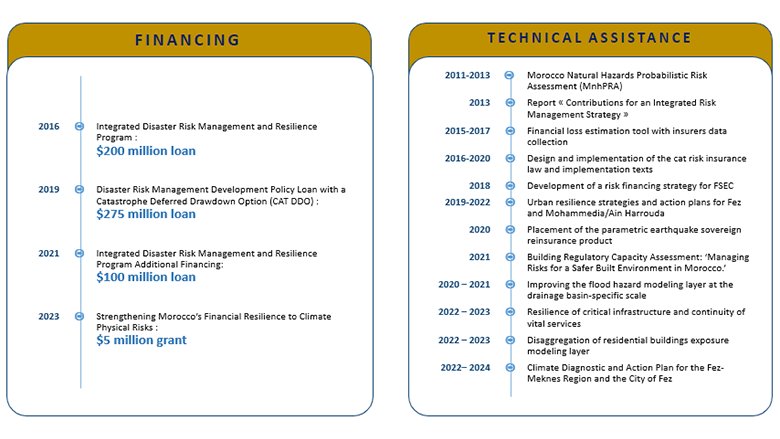
Over the last 15 years, the World Bank has been supporting the Moroccan government’s efforts to strengthen the country’s disaster and climate resilience. Through several operations and technical assistance activities, the World Bank has supported a shift in government policy from focusing on ex-post emergency response toward a more integrated disaster risk management (DRM) approach with a strong focus on ex-ante disaster risk reduction and financial preparedness. Three World Bank operations, representing a total amount of $580 million, have promoted institutional reforms, capacity strengthening, risk reduction investments, and the establishment of a comprehensive disaster risk finance and insurance regime. These operations have been complemented by a range of technical assistance activities around issues such as urban resilience, critical infrastructure resilience, strengthening the building regulatory environment, and disaster risk finance (DRF).
Results:
Over the last 15 years, the World Bank has supported the government of Morocco in fundamentally changing its DRM/DRF system, moving from a reactive approach focused on ex-post emergency response toward a preventive, ex-ante resilience-building approach. This evolution is benefiting the entire population of Morocco. Results achieved encompass five main areas:
- Disaster risk reduction. Between 2016 and 2024, the World Bank supported the financing and implementation of more than 230 disaster risk reduction projects, worth $304 million, through the redesign of Morocco’s Fund for the Fight against Natural Catastrophes (FLCN), from an emergency response vehicle into a national resilience fund. Among others, these projects include flood protection investments, early warning systems and disaster risk mapping. So far, completed projects have benefited around 400,000 direct beneficiaries, and over 33 million indirect beneficiaries across the country.
- Institutional strengthening. In 2020, the government of Morocco created a new Directorate for Disaster Risk Management within the Ministry of Interior, with clear lines of responsibility. Institutional capacity has been gradually increased and the Directorate now employs more than 80 full-time staff. In 2021, the government adopted its first National Disaster Risk Management Strategy (2021–2030). The strategy has been translated into a priority action plan (2021–2023) and an operational action plan (2021–2026) that covers 18 programs and 57 projects currently under implementation (including, for example, disaster awareness campaigns; support for public-private investments in risk reduction; strengthening resilience of critical public networks).
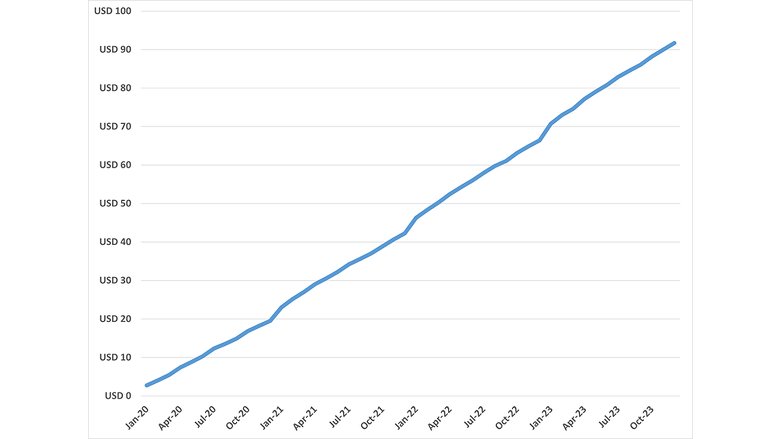
- Financial protection. In 2016, the government adopted an innovative disaster risk insurance regime (Law No. 110-14), which became effective in January 2020. The law introduced a private insurance scheme covering more than 17 million people. To complement this scheme, the government also established a public solidarity fund (FSEC) to cover the remainder uninsured population, including poor and vulnerable households unable to afford private insurance. A parafiscal tax on private non-life insurance contracts has funded FSEC’s operations and reserves, with more than $90 million collected for calendar years 2020 to 2023. Following the Al-Haouz Earthquake that occurred on September 8, 2023, the FSEC unlocked approximately $300 million to cover eligible losses, out of which $275 million came from sovereign reinsurance placed in 2020 and renewed in 2023.
- Disaster preparedness. A newly created flood risk early warning system (“Vigirisque Inondations”) has been operational since 2023 in four pilot areas (Mohammedia, the Gharb region, the Ourika valley, and Guelmim province), directly benefiting an estimated 240,000 people. The civil protection system has continuously strengthened its human resources through improved training and education, and increased staffing. Finally, a draft national directive and practical guide to strengthen the resilience of critical infrastructure and essential services were developed through inter-ministerial collaboration among more than 30 government institutions.
- Risk understanding. In 2012, Morocco developed a catastrophe risk model, the Morocco Natural Hazards Probabilistic Risk Assessment (MnhPRA), which allows for the estimation of the economic impact of disasters (earthquake, flood, tsunami, drought, and landslide). Since 2021, the FSEC has been conducting additional disaster risk modeling efforts to estimate the financial costs of earthquake, flooding, and landslides. The government has also piloted urban resilience diagnostics and strategies for the cities of Fez and Mohammedia/Ain Harrouda, an approach that can be replicated in other municipalities. A National Risk Observatory within the DRM Directorate is currently being strengthened and fully operationalized.
Data Highlights
Value of financed and completed FLCN projects from 2016 to 2023 (US$)
Cumulative revenue from parafiscal tax on private non-life insurance collected for FSEC (expressed in million USD)