News and stories from our partners
Global Program on Sustainability
Partners
-
Core Implementing Country

Development of Natural Capital Accounts, Data, Tools, and Analyses
Significant progress has been made in delivering grant activities and achieving results in FY24. The finalization of the land-use/land-cover classification has been a major milestone, providing the necessary data to complete the land accounts. The land accounts are scheduled to be published within the next six months, contributing valuable information to the understanding of land resources in Ethiopia. Efforts are under way to compile the data for the land degradation assessment and the preliminary ecosystem services and extent account. Spatial data on national-level land degradation has been prepared to serve as an input for the IPT in coordination with the IPT technical working group. Similarly, national-level biophysical data on soil retention, water, and carbon regulation services has been compiled as key criteria under the IPT. This data will be the basis for preparing the ecosystem extent and services accounts.
Another notable achievement is the completion of a second version of the IPT for watershed selection in close coordination with the Ministry of Agriculture, as well as a guidance note on the inputs to the tool and the tool’s uses. The underlying data and IPT are available to government partner agencies and members of the Climate Action Through Landscape Management team, enabling relevant stakeholders to access and use the tool for informed decision-making and strategic planning. The draft report on mainstreaming NCA in Ethiopia is progressing well, with the final version expected to be finalized for consultation by December 2024. This report will incorporate initial lessons from all the missions conducted to date, the institutional and data assessment, and progress on natural capital accounts and linkages to IPT, as well as outline ways to mainstream NCA applications.
Informing Investments and/or Policies
The Ethiopia CIC program has played a crucial role in informing the Climate Action Through Landscape Management Project, a World Bank lending project with a budget of US$500 million. The grant team has specifically developed an updated version of the Investment Prioritization Tool (IPT v2) to support watershed selection under this program, building upon the previous work conducted for the Ethiopian Strategic Investment Framework. The grant team has collaborated closely with the program technical team in the country and the Ministry of Agriculture and built capacity to use the tool and data.
The grant activities have made valuable contributions to the development of the Payment for Ecosystem Services Proclamation. The grant team has been actively involved in reviewing several versions of the proclamation and providing direct inputs to the text. It is anticipated that the proclamation will be approved by the Council of Ministers later in 2024, marking a significant step toward promoting the sustainable management of ecosystems and the services they provide. The grant team used the modeling work conducted by the IPT to identify criteria and key watersheds for investment to influence the revision of the Ethiopia Sustainable Land Management Strategic Investment Framework (ESIF2). Moreover, the grant-supported ecosystem service modeling was included in the CCDR.
Capacity Building and Institutionalization
A wide range of public sector entities have actively engaged with this initiative. These entities include the National Council on Climate Change Secretariat; Ministry of Finance; Ministry of Budget and Economic Planning; Ministry of Environment; Ministry of Agriculture and Food Security; National Bureau of Statistics; Energy Commission; Ministry of Petroleum Resources; Ministry of Industry, Trade, and Investments; National Mapping Agency; Nigeria Governors’ Forum; and the state governments of Nasarawa and Kaduna. To ensure capacity building and knowledge transfer, two hands-on training courses and four workshops were conducted in FY24. These sessions covered various topics relevant to the grant activities, including an introduction to land accounts, the System of Environmental-Economic Accounting, and ecosystem accounts, policy interventions to address agriculture-driven deforestation in Nigeria, tree-cover loss analyses, diversification with mitigation outcome scenarios, and land-use and land-cover classification. The workshops and training sessions saw a decent participation from women, with attendance of between 23 percent and 50 percent for each session.
Communication
As mentioned above, the final policy inception note was prepared for the National Council on Climate Change and sent to the President. The Council would like to use the policy paper to start a debate about how to position Nigeria in the next COP as regards “a just and equitable transition away from fossil fuels”. A workshop on policy interventions to address agriculture-driven deforestation in Nigeria enhanced the dialogue of the World Bank and other partners with the federal government and states on how to address drivers of deforestation and increase access to clean cooking.
Learn more about GPS's work in Ethiopia
-
Core Implementing Country

Development of Natural Capital Accounts, Data, Tools, and Analyses
The development of natural capital accounts has made significant progress this fiscal year, with the completion of the Land and Ecosystem Extent Accounts. The reference data and methodology used in developing the wealth and adjusted macroeconomic indicators were published. These datasets are publicly accessible and can be found on the Ghana Environmental Protection Agency website. The Land and Ecosystem Extent Accounts are being produced, including the compilation of underlying maps, data sets, and change matrices. These accounts will be peer reviewed by the United Nations Statistics Division and will be finalized and published by December 2024.
Considerable progress has been made in producing the Ecosystem Services Accounts. The data compilation is complete for provisioning ecosystem services, such as wood-fuel, timber, and non-timber forest products, as well as regulating ecosystem services like carbon retention and climate regulation. However, data is still being compiled on population, poverty incidence, household expenditure, and water-related ecosystem services. This information is crucial for developing a robust ecosystem services account.
Informing Investments and/or Policies
The Ghana CIC program provided support to the Ghana Landscape Restoration and Small-Scale Mining Project in producing a relevant set of land and ecosystem extent maps and change matrices for one district in December 2023. This successful work is now being replicated in 11 pilot project districts, with the CIC program team offering quality assurance support to inform efforts by the project in piloting the creation of spatial development frameworks at the district level. The assistance provided by the CIC program has been acknowledged in the project’s implementation support mission.
Progress has also been made towards informing two significant policy documents. The National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan will outline Ghana’s strategy for addressing biodiversity threats and ensuring the conservation and sustainable use of its biodiversity. The National Medium-Term Development Policy Framework sets out Ghana’s medium-term goals, objectives, and targets, serving as the foundation for the preparation and implementation of development plans by ministries, departments, and agencies. In FY24, a mapping exercise was initiated to determine how the land, ecosystem extent, and ecosystem services accounts can be used to establish national targets under the Global Biodiversity Framework. Although there is ongoing dialogue, the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan process is now supported by the United Nations Development Programme and the World Bank is encouraging the use of NCA data to inform the process. To inform the National Medium-Term Development Policy Framework, a roadmap is being prepared to integrate biodiversity and NCA into national and regional development planning processes. A draft concept note outlining this plan has been prepared and shared with the World Bank. Furthermore, an explanatory note is being prepared to guide ministries, departments, and agencies on how to incorporate key findings from the grant activities into their respective medium-term development plans. This note will help ensure that the valuable insights gained from the CIC program are effectively integrated into the planning processes of various ministries, departments, and agencies.
Capacity Building and Institutionalization
Efforts are being made to institutionalize NCA and promote awareness and understanding of the concept. As part of these efforts, a practical training session on the production of accounts was organized in September 2023. This training spanned five days and had 29 participants, including five women, with eight government agencies represented. While GPS actively encourages the participation of women in such training, final selection by government agencies is often based on seniority or prior engagement in a given area and few women get selected. In March 2024, nine participants including five women from five key partner agencies participated in the Global Policy Forum on NCA in Rwanda. To further strengthen the government’s capacity to institutionalize NCA in relevant government policies and investments, a study tour was organized. This tour aimed to facilitate the exchange of ideas and experiences related to NCA for decision-making and policy making.
To strengthen information flow and coordination, the team continues to engage with other development partners like the Food and Agriculture Organization, the government of Denmark (Statistics Denmark), and the United Nations Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre, which are supporting different aspects of Ghana’s NCA program. The team also met with the United Kingdom’s Office of National Statistics to discuss available data and identify potential synergies with the World Bank/GPS-funded accounts.
Communication
As noted, representatives from government agencies participated in the Global Policy Forum on NCA in Rwanda. During the forum, the officials had the opportunity to share the outcomes and experiences from the Ghana CIC program. This was done through panel discussions, poster presentations, displays, and involvement in the CIC workshop, among other means.
Ghana’s Natural Capital Accounting program trains local journalists and Civil Society Organizations

Ghana’ s Natural Capital Accounting (NCA) program is currently developing and finalizing its land and ecosystem extent, as well as ecosystem services accounts, and discussing the application of these accounts in policy and investment decisions. The accounts are expected to be published by early 2025.
As part of the capacity building engagements under the program over 50 journalists and civil society organization (CSOs) representatives were trained at a one-day capacity-building workshop on NCA in Accra on 6th of August, 2024. The overall objective of the engagement was to equip the media and civil society with the knowledge and skills necessary to understand, interpret, and effectively communicate as well as advocate for NCA.
In her welcome remarks, Dr Ofosu-Baadu, Chief Statistician at the Ghana Statistical Service (GSS) and National Co-Coordinator, Ghana NCA Program, said the challenges posed by global climate crisis, biodiversity loss and other environmental excesses made the adoption of NCA crucial. “When NCA is mainstreamed into the country's economic accounting system, it would help to accurately measure the assets and liabilities of the nation’s natural resources for sustainable development”, she said. She therefore appealed to stakeholders, particularly the media and CSOs to work with state institutions in championing the NCA process, to help influence decision-makers and mainstream it into development policies.
In separate statements, the Director of Development Coordination at the National Development Planning Commission (NDPC), Dr Winfred F. A Nelson; the Deputy Executive Director of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Abu Abdul Hanan, and the Director of Economic Statistics at the GSS, Edward Asuo Afram, representing the three NCA coordinating institutions, highlighted the need for the media and civil society organizations (CSOs) to work closely with the state institutions to preserve the country's natural resources for future generations.
Mr. Hanan said “we consider the media and CSOs to be our strategic partners in this NCA journey and the broader environmental protection mandate. The media, for instance, have a crucial role in setting the agenda and communicating the importance of Natural Capital Accounting to all relevant stakeholders.” Mr Afram believes that forests, wildlife, biodiversity and minerals are critical resources that needed to be adequately measured and accounted for whilst Dr. Nelson called for an urgent need for sustainable development, stating that evidence-based advocacy is essential to influence decision-makers.
The workshop also had some technical presentations on the overview of NCA program in Ghana, on the policy relevance of NCA in sustainable development, and on NCA for media and advocacy. The apex of the training was a panel discussion on Leveraging Natural Capital Accounting for Sustainable Development in Ghana: Challenges, Opportunities, and Effective Communication Strategies. This in-depth discussion focused on the current state of NCA in Ghana, the challenges and opportunities in implementing NCA for sustainable development in Ghana, practical strategies for communicating NCA concepts and findings to various stakeholders and potential collaborations between government, media, and CSOs in promoting and implementing NCA.
Learn more about GPS's work in Ghana
-
Core Implementing Country - Nepal
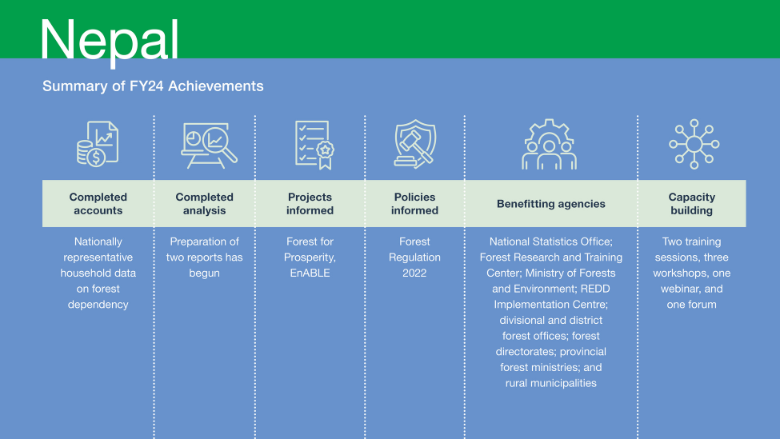
Development of Natural Capital Accounts, Data, Tools, and Analyses
Remarkable progress has been made in the compilation of data for the socioeconomic and biophysical forest data sets in FY24. The nationally representative socioeconomic forest data compilation (which was done in parallel with the Fourth Nepal Living Standards Survey) has been completed, and the data will be published and made publicly available by the Nepal National Statistics Office in FY25. This data set is informs a report which aims to provide valuable insights into the relationship between households and public forests and private trees, mediated by consumption expenditure. The report will be completed in FY25.
In parallel, progress has been made in compiling the biophysical forest data. Using remote-sensing data and ground-truthing techniques, the draft data set has been completed. The data will be finalized, published, and made publicly availableby the Forest Research and Training Center in FY25. Similarly, this data set will be the basis of a report on the spatial distribution of forests by forest type and analysis of forest fragmentation at the level of municipality. The report is also scheduled to be completed in FY25.
Informing Investments and/or Policies
GPS-supported activities played a key role in informing two World Bank lending projects in FY24, namely Forests for Prosperity andEnABLE. In the Forests for Prosperity project, the GPS work supported implementation by providing analytical inputs to design additional and restructure existing interventions. The GPS-supported socioeconomic analysis on forests made a compelling case for supporting afforestation and tree planting on private and public land to support livelihoods. The analysis found that 37 percent of Nepali households accessed public forests mostly to collect firewood, grass, and leaf litter, with the largest share of public forest users being the poorest. This suggested that efforts to strengthen community forestry initiatives would benefit the poor. Importantly, 48 percent of Nepali households had private trees for non-timber forest products, with the incidence of private tree ownership uniformly distributed across richer and poorer households. This suggests that supporting private tree planting may enhance the livelihoods of all rural households and reduce pressure on publicly managed forests. These insights were used to expand tree planting to private lands under the Forests for Prosperity lending project. GPS-supported analytics provided inputs to the design of the EnABLE project, identifying ways in which indigenous people, women, and minorities could be supported to share in the benefits derived from forest improvements.
The analysis showed that a higher proportion of community forest users belong to the poorest households and that community forests held relatively greater importance for the livelihoods of the poor. These insights have informed the 2022 Forest Regulation, which now includes special provisions for poor and female-headed households seeking access to community forests. The analytics also showed that private trees are important for the livelihoods of all households, especially in rural areas. The 2022 Forest Regulation now classifies forest products from private trees as agroforestry products to remove barriers in the movement of these products and support incomes and livelihoods. These policy changes ensure greater equity and inclusivity in forest management practices. Furthermore, the subnational biophysical forest data, which is being collected through GPS supported activities, will support the implementation of the Federal Equalization Grant Policy under the National Natural Resources and Fiscal Commission Act. In FY24, draft data sets were produced in close collaboration with the Forest Research and Training Center, which is mandated to provide this data to the Commission.
Capacity Building and Institutionalization
To deepen the understanding of poverty and environmental statistics among government officials, two training sessions were conducted in Bangkok and Washington, DC, in FY24. These sessions brought together participants from relevant government agencies such as the National Statistics Office, Forest Research and Training Center, and Ministry of Forests and Environment. Additionally, three workshops focused on engaging stakeholders at the local level and gathering valuable inputs regarding biophysical forest indicators were organized in the provinces of Lumbini, Madhesh, and Koshi. This participatory approach ensured that the data produced reflect the perspectives and priorities of the local communities, promoting inclusivity and ownership in the decision-making process. The data production efforts supported by the Nepal CIC program are led by the National Statistics Office and Forest Research and Training Center, ensuring that the government takes ownership of the process. The GPS team collaborates with other key partner agencies including the Ministry of Forestry and Environment, REDD Implementation Centre, divisional and district forest offices, forest directorates, provincial forest ministries, and rural municipalities.
Communication
On November 14, 2023, a seminar was organized to showcase the findings and share experiences from implementing the Nepal CIC activities. This seminar served as a platform to disseminate the knowledge and insights gained through the program. The event provided an opportunity for stakeholders, experts, and interested parties to engage in discussions and learn from the experiences shared during the seminar. Nepali delegates played an active role in the GPS Global Policy Forum held in Rwanda. They participated in various activities, including engaging in panel discussions, displaying posters, and delivering presentations. Participating in this Forum allowed them to share their expertise and experiences as well as network with participants from other countries. The CIC workshop held with the GPS Global Policy Forum further facilitated dialogue and collaboration among key stakeholders. The workshop provided a focused space for sharing experiences, best practices, and lessons from the Nepal CIC program, fostering cross-learning and the exchange of innovative ideas.
Learn more about GPS's work in Nepal:
- Enabling evidence-based sustainable forest management for Green, Resilient, Inclusive Development in Nepal
- Improving Data and Analytics for Sustainable Forest Management in Nepal
-
Core Implementing Country - Türkiye
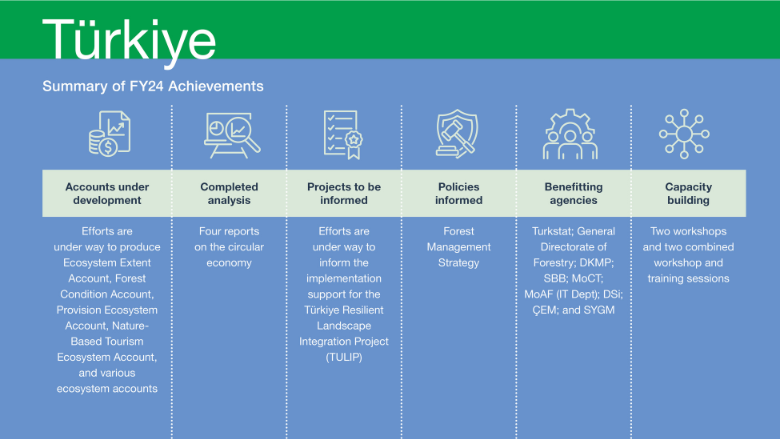
Development of Natural Capital Accounts, Data, Tools, and Analyses
The production of various accounts is under way. Specifically, data has been collected, drafts have been compiled, and results have been discussed for the Ecosystem Extent Account, Forest Condition Account, Provision Ecosystem Account,
and Nature-Based Tourism Ecosystem Account. In addition, discussions on data requirements and methodologies have taken place for multiple ecosystem accounts. These include the Global Climate Ecosystem Account, Soil Retention Ecosystem Account, Crop Provision Ecosystem Account, and Flood Control Ecosystem Account. These efforts are crucial in providing accurate and reliable information for the accounts’ production. In FY24, significant progress was made in completing four circular economy reports. These reports have been submitted to the client for review and approval. Most institutions have already provided their feedback and the team is organizing two dissemination events to be held in Istanbul in the second quarter and Brussels (date to be confirmed)
The four reports are as follows:
- Circular Economy Transition in Türkiye: Impacts and Interactions. This report analyzes the macroeconomic impacts of circular economy policies in Türkiye and addresses the complementarity between these and climate policies, examining the impacts of targeted circular economy policies on key factors such as economic growth, the labor market, and welfare. It provides recommendations on policy actions and measures to mitigate any potential negative impacts.
- Türkiye’s Circular Economy Transition in the EU’s GVC Ecosystem. This report assesses the exposure of Türkiye’s industry to evolving circular economy policies in major trade partners. It explores the connection between trade and material use in Türkiye, assessing how regulatory differences with the European Union affect Türkiye’s competitiveness in various industries. It provides recommendations on trade and investment policy, human capital development, supplier development programs, standard development, compliance, and infrastructure requirements.
- Building a Competitive Circular Economy: Prioritizing Industries for Accelerated Development in Türkiye. This report identifies the sectors and industries that are crucial for adopting circular economy strategies and achieving resource efficiency in critical materials. It suggests measures to support these sectors and industries. The analysis includes an assessment of sector and network linkages, identification of potential and gaps, and recommendations for the emergence of circular business models.
- Economic, Trade, and Industry Implications of the Circular Economy Transition in Türkiye. This summary report provides an overview of the three aforementioned reports and highlights the key findings and recommendations, offering a consolidated view of Türkiye’s circular economy.
Informing Investments and/or Policies
The Turkish CIC program is supporting the implementation of the Türkiye Resilient Landscape Integration, a US$135 million project. The project objective is to strengthen integrated landscape management and increase access to improved livelihood opportunities and resilient infrastructure services for rural communities in targeted areas of Türkiye. Activities under the grant supported project implementation by conducting preliminary analysis to assess the benefits of livelihoods supported by the project for different stakeholder groups in the context of natural resource management. This analysis was carried out through focused group discussions, enabling a comprehensive understanding of the potential impacts and advantages of the project. The CIC program also provided pilot ecosystem accounts for two watersheds under the project. These accounts are valuable for evaluating and monitoring the ecological status of these areas, contributing to effective landscape management.
GPS-sponsored activities in Türkiye have had significant impact on two government policy documents—the Forest Management Strategy and the Circular Economy Strategy and Action Plan.9 The draft of the General Directorate of Forestry’s Strategic Plan (2024–2028) was revised to include Forest Ecosystem Services after GPS-NCA works. Currently the national accounts do not value the goods and services from the forest sector. The General Directorate of Forestry is interested in improving forest ecosystem services and initiated a new project on “valuation of ecosystem services” to gain experience and know-how. The General Directorate of Forestry needed to integrate international methodologies and standards for NCA (especially the United Nations System of Environmental-Economic Accounting) in order to improve and disseminate its work. The GPS-NCA project allows the General Directorate of Forestry to improve its technical capacity in the System of Environmental-Economic Accounting, among others. This revised plan has recently been published, highlighting the importance of integrating biodiversity and ecosystem services into forest management. The Circular Economy Strategy and associated Action Plan are in the final phase of preparation, and the GPS-funded analysis has played a vital role in the development of these documents. Furthermore, the CIC program team has engaged in discussions with TurkStat, emphasizing the significance of including NCA as part of official national statistics. As a result, TurkStat has committed to including NCA in the Official Statistics Program 2024 under the category of “Future Statistics,” indicating its planned implementation in the coming years.
Capacity Building and Institutionalization
In FY24, efforts were made to enhance understanding and build capacity in NCA and related methodologies produced in Türkiye. This was accomplished through the organization of two workshops and two combined workshop and training sessions. These workshops and training sessions were designed to bring together government officials from key agencies involved in natural resource management to foster collaboration and ensure a comprehensive understanding of NCA among key stakeholders. Efforts were made to ensure gender inclusivity in these events with the proportion of female participants ranging between 28 and 37 percent.
Communication
Counterparts for all work streams have been engaged through regular meetings. Regular discussions and sharing of findings related to the circular economy were held with the Ministry of Trade. In addition, SBB, MoIT, CSB, and TÜBITAK reviewed the circular economy reports and provided comments. The Ministry of Trade will also facilitate the organization of the two dissemination workshops to be held in Istanbul and Brussels. For NCA work, the biophysical and spatial data needs and protocols for data sharing were discussed with TurkStat, which is the agency responsible for publishing statistical data. The roadmap for developing NCA work was finalized through consultative meetings with the General Directorate of Forestry and TurkStat. A specialized resource firm, Vlaamse Instelling voor Technologisch Onderzoek, was contracted based on the recommendation of United Nations Statistics Division experts in November 2023 to finalize the development of natural capital accounts, including training and capacity development for national partners (the General Directorate of Forestry and TurkStat). The contract will end in December 2024.
Enhancing Women Participation in Livestock Production In Turkiye

The Global Program on Sustainability helped to investigate the interests of women in rural Turkiye and the opportunities they foresee for themselves in better landscape management. The Social Inclusion work focused mainly on women’s role in the use of natural resources, farming, livestock rearing and forestry, their assessment of the status of the natural resource base in their villages, and their outlook on the future of their livelihoods in Turkiye. The discussions focused on villages in Bolaman and Çekerek Basins, since women are heavily involved in farming, livestock management, and hazelnut production – main uses of natural resources in these two basins.
Focus Group Discussions (FGD) were conducted with 257 people in total in 16 exemplary villages in Bolaman and Cekerek basins (7 in Ordu Province and 9 in Yozgat Province). There was a 50% participation rate of women in the FGDs.
The 50% participation rate itself is an indicator that decisions on women’s livelihoods are made jointly by men and women and that voices of women can be strengthened in the context of natural resource management, and women are willing to take on decision making if provided the relevant platforms to do so. The findings of FGDs, show that women are highly interested in increasing the number of livestock and undertake livestock management for commercial production of dairy and meat products amongst others contrary to perception that livestock management is male dominated venture. The key areas where they need support are establishing women cooperatives for better marketing, processing facilities and trainings. However, high feed prices, low product prices and lack of labor are the limiting factors.
In order to adapt to climate change and increase productivity in crop production, women are willing to be supported in different types of crop production compatible with the changing climate and regional characteristics, with high value (greenhouses, medicinal aromatic plants, mushroom species with high market value, special niche products such as aronia, truffles, chestnut honey, other herbal and medicinal plants to market) besides increasing and strengthening agricultural mechanization, and marketing opportunities.
-
Core Implementing Country - Bangladesh
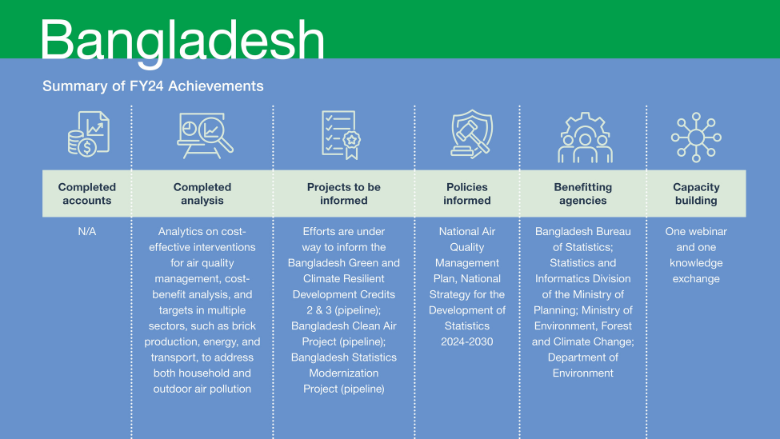
Development of Natural Capital Accounts, Data, Tools, and Analyses
Building on the recently concluded TTA, the Bangladesh CIC program aims to enhance the capacity of the government in environmental management and to pilot new financing mechanisms to promote green investments in targeted sectors. To achieve this objective, the program intends to produce three analytical reports that will inform relevant policies and lending projects. Significant progress has been made in this regard, with the completion of the first report on cost-effective interventions, the cost-benefit analysis, and targets in multiple sectors. This report addresses the issue of indoor and outdoor air pollution, focusing on sectors such as brick production, energy, and transport. It has been published externally as part of the Bangladesh Country Environmental Analysis 2023.
The second report, currently in the inception stage, is a feasibility study that assesses investment opportunities in the Sundarbans. This study also examines the economic case for natural capital-based coastal resilience. The terms of reference for conducting the study were finalize in FY24 and a firm has been selected through acompetitive process. The final study is expected to be delivered in FY25.
The third report, which focuses on developing a Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) framework for greenhouse gas emissions, is being finalized. The task team presented the initial findings of this report to the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change and the Department of Environment. However, the Bangladeshi government has decided to prioritize the development of a continuous emissions monitoring program instead of an MRV system. The program will track air pollutant emissions from major point sources (stacks), with regular disclosure of preliminary data and immediate enforcement of emissions standards by the Department of Environment. Consequently, the indicative trigger for the third Bangladesh Green and Climate Resilient Development Credit has been adjusted. The findings of the MRV report will support the adoption of a key air quality management policy, particularly as the basis for carbon-pricing instruments—but this policy will not be finalized within the trust fund grant timeline. Nevertheless, the MRV report will be valuable in the future when combined with additional data on emissions sources for assisting the government in designing a carbon-pricing instrument, such as an Emissions Trading System. Furthermore, the MRV framework will support the systematic reporting of natural capital-based greenhouse gas emissions.
Informing Investments and/or Policies
The analysis conducted as part of the 2023 Country Environmental Analysis (CEA) has played a crucial role in shaping the National Air Quality Management Plan. This plan outlines specific interventions to be implemented across targeted sectors by 2030 to improve air quality in Bangladesh. The plan recognizes the impact of transboundary emissions and emphasizes the importance of collaboration with other countries in the Indo-Gangetic Plains and Himalayan Foothills region. The plan is scheduled for approval in July 2024 and is expected to influence the design of two World Bank lending projects: the second Green and Climate Resilient Development Credit and the Bangladesh Clean Air Project. The activities on the MRV system on short-lived climate pollutants will be financed by the Clean Air Project. However, the TTA support (initiated before the CIC grant) informed the Bangladesh Sustainable Coastal and Marine Fisheries Project. The fisheries data gap analysis financed by GPS was used to inform the implementation of this project. The activities supported by GPS also contributed to the National Strategy for the Development of Statistics 2024-2030. Through tailored advisory services, the GPS team helped incorporate and strengthen a dedicated section on environmental statistics, including recommendations for NCA, in the updated strategy. Environmental statistics was also identified as one of the strategic priorities in the revised strategy. The advisory services provided through international experts and a high-level visit to Washington, DC, were instrumental in shaping the initial engagements on the Bangladesh Statistics Modernization project. Specifically these inputs contributed to the creation of a dedicated sub-component focused on environmental statistics and NCA and will be fully reported in future when the project is approved. Such advisory services from GPS will continue to support this project in FY25. Efforts are under way to use the MRV report and the feasibility study on the economic case for nature-based coastal resilience to inform the Bangladesh Green and Climate Resilient Development Credit-3, Bangladesh Clean Air Project, and the Bangladesh Coastal Resilience Project.
Capacity Building and Institutionalization
A five-day knowledge exchange was conducted between June 24 and June 28, 2024, where a high-level delegation from the Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics and the Statistics and Informatics Division of the Ministry of Planning visited Washington, DC, to exchange experiences, knowledge, and lessons with the World Bank and the United States government on efforts to modernize statistics, particularly on the environment, gender, and poverty.
Communication
On June 25, 2024, a GPS seminar was organized with more than 60 participants on the role of data and statistics in addressing Bangladesh’s environmental challenges. The seminar drew from the results of the Technical Assistance in Bangladesh to highlight the critical role that data and statistics play in fostering sustainable development in Bangladesh. Officials from the Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics and the Statistics and Informatics Division were instrumental in organizing the seminar.
Learn more about GPS's work in Bangladesh
-
Core Implementing Country - Nigeria

Development of Natural Capital Accounts, Data, Tools, and Analyses
The CIC program in Nigeria has a clear objective: to provide support for the country’s planning and implementation of climate change mitigation and adaptation commitments, while enhancing its water security and environmental management policies. To achieve these goals, the program is producing three natural capital accounts—land, ecosystem, and greenhouse gas—and conducting two economic analyses. In FY24, a significant milestone was reached as the accounts were completed. They will be published and made publicly available in the forthcoming months. Additionally, an analysis was finalized that focuses on tree-cover loss, assessing the key drivers and impacts of deforestation and forest degradation. A policy note and modeling work for the report on Nigeria’s diversification strategies under the global low-carbon transition, supported by the CGE model ENVISAGE, were also completed and validated by relevant stakeholders.
Informing Investments and/or Policies
Efforts are under way to enhance the implementation of the Agro-Climatic Resilience in Semi-Arid Landscapes project. The primary objective of this project is to support the adoption of sustainable landscape management practices in targeted watersheds in northern Nigeria and strengthen the country’s long-term capacity for integrated climate-resilient landscape management. GPS work will inform the strategic watershed plans and selection of investments in Nasarawa and Kaduna. Data and maps produced for the ecosystem accounts are being used by the project team preparing the catchment management plans and are hosted in the project coordination units on federal and state levels.
In terms of policy impacts, policy notes and impact assessments related to diversificatio strategies under the global low-carbon transition developed through grant activities are contributing to updates of three national plans: the National Development Plan, the National Climate Change Action Plan, and the Energy Transition Plan. To further support policy changes, a policy inception note was prepared for the National Council on Climate Change Secretariat and sent to the President. The final policy note was shared with the new management of the Secretariat, which intends to use the policy paper in the next Conference of the Parties (COP) to support a “just and equitable transition away from fossil fuels”. In April 2024, a national policy on clean cooking was approved, marking a significant step towards sustainable energy usage. Following this approval, the government will begin preparing a national program on clean cooking. It is expected that the analysis of tree-cover loss, conducted as part of the CIC work, will inform this program, and potentially influence a new World Bank lending operation, currently under discussion, centered on forestry and clean cooking. A new analysis on understanding the relationship between wood fuel consumption, gender, and poverty to decrease the impacts on ecosystem degradation in Nigeria is ongoing and will be finalized in December 2024. The tree-cover loss analyses and policy note on transition risks to low-carbon growth will underpin the narrative in the upcoming CCDR that is planned to be completed within FY25.
Capacity Building and Institutionalization
A five-day knowledge exchange was conducted between June 24 and June 28, 2024, where a high-level delegation from the Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics and the Statistics and Informatics Division of the Ministry of Planning visited Washington, DC, to exchange experiences, knowledge, and lessons with the World Bank and the United States government on efforts to modernize statistics, particularly on the environment, gender, and poverty.
Communication
On June 25, 2024, a GPS seminar was organized with more than 60 participants on the role of data and statistics in addressing Bangladesh’s environmental challenges. The seminar drew from the results of the Technical Assistance in Bangladesh to highlight the critical role that data and statistics play in fostering sustainable development in Bangladesh. Officials from the Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics and the Statistics and Informatics Division were instrumental in organizing the seminar.
-
Targeted Technical Assistance - Cambodia

The GPS-funded grant “Enhancing Natural Resource and Pollution Management in Cambodia” is closely aligned with the country’s priorities and strategic focus on nature-based solutions. This enables the integration of nature-based solutions principles into various sectors such as transport/roads, agriculture, water, tourism, urban development, and water supply and management.
Regarding outputs, ecosystem accounts were developed for two selected watersheds in Cambodia: the Stung watershed and the Kantout watershed. The process involved comprehensive steps including baseline profiling, hazard and climate change impact assessment, vulnerability assessment, resilience-building strategy development, and ecosystem services valuation. These efforts culminated in the identification assessment, and prioritization of nature-based solutions in the two watersheds. The hazard and climate change impact assessments conducted in these areas provided a foundational understanding of socioeconomics, hydrology, natural systems, hazards, and climate dynamics. The assessments also evaluated the potential impacts of flood agricultural drought, and water scarcity on key agricultural assets and areas of interest in the context of climate change. The use of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool facilitated the creation of hydrological models for both watersheds, aiding in understanding hydrological patterns, selecting potential solution sites, and projecting the impact of proposed solutions on watershed hydrology. These assessments and modeling efforts contributed to the development of the report Assessing the Potential of Nature-Based Solutions for Increasing Water Security in Selected Watersheds, Cambodia. This report was shared with relevant ministries to underscore the significance of nature-based solutions in enhancing climate resilience, thereby offering concrete policy recommendations to the government.
GPS-funded activities have informed the activities relating to nature-based solutions in the Cambodia Water Security Improvement Project. The study’s target areas were specifically identified through engagement with the Ministry of Water Resources and Meteorology, the project’s lead implementation agency, to support the identification of priority vulnerable areas and potential measures. These results were integrated into the project design during project development. The project’s interventions are designed using a nature-based approach, which provides a combination of adaptation and mitigation benefits while also reducing greenhouse gas emissions. A combination of structural, including nature-based solutions, and non structural adaptation solutions will be implemented where appropriate. Specifically, under Subcomponent 1.3, River Basin Management Plans will be developed, which will create an avenue for integrating a nature-based planning approach, involving the conservation of existing natural assets and the incorporation of nature based solutions to reduce flood and drought risks. Subcomponent 2.1 will also finance the preparation of feasibility studies, engineering designs, and construction activities, including the integration of nature-based solutions for increased flood and drought risk management. The project was approved in June 2024. The objective of the project is to improve aspects of water security and to increase agricultural water productivity in selected river basins of Cambodia.
The analytical work conducted informed policy via the Environment and Natural Resources Code of Cambodia (Ministry of Environment) and revision of the Law on Forestry (2002) (Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry & Fisheries) and associated policies. This was achieved by framing nature based solutions analysis around specific components of the legislation and government policy imperatives, and by workshops with both ministries to discuss nature-based solutions analysis and approaches. Additionally, the knowledge generated through this ASA work enabled the World Bank Task Team to carry out informed consultations with the Ministry of Environment and Ministry of Water Resources and Meteorology on enhancements to the Environment and Natural Resources Code.
-
Targeted Technical Assistance - India

The GPS-sponsored grant in India was established to assess the impact of nature-smart and climate resilient policies in India using macroeconomic and land-use models that incorporate natural capital and ecosystem services. In FY24, activities supported by the grant resulted in the completion of two analytical pieces: Integrating Natural Capital in Evidence-Based Public Policy Making in India and Nature-Based Solutions for Resilience, Adaptation, and Mitigation Benefits Against Climate Change. The study on integrating natural capital in evidence based public policy making enhanced the understanding of the economic implications of forestry-based carbon mitigation policies in India within the framework of its NDC and long-term mitigation objectives. Through the dynamic Integrated Economic-Environmental Modeling approach coupled with high-resolution spatial Land Use Land Cover change and Ecosystem Services modeling, the study evaluated how various policy scenarios would affect changes in land use, ecosystem services, wealth, and gross domestic product. The analytical piece on nature-based solutions for resilience, adaptation, and mitigation benefits against climate change estimated the number of person-days that could be generated if the NDC targets for carbon sequestration are met. In FY25, the key findings from these studies are expected to be submitted to an academic journal, and a dissemination workshop in collaboration with the Indian government is also planned.
Thus far, the first study has contributed to India’s country economic memorandum and informed its CCDR, which is under preparation, by offering a quantitative analysis of the economic implications of forestry-based carbon mitigation actions and the flow of ecosystem services. The second study has also informed the CCDR by providing a quantitative assessment of the land and cost requirements for achieving the forest-related carbon sequestration targets outlined in India’s NDC. Both studies have contributed to India’s Streamlined Systematic Country Diagnostic Update 2024 (to be completed by the end of 2024).
The analytical work is informing the design of two projects, namely the Transformational Restoration for Ecological and Economic Development and the Enhancing Landscape and Ecosystem Management projects. The Transformational Restoration for Ecological and Economic Development project, a multi-state forestry initiative, aims to support India in meeting its carbon sequestration targets under its NDC. While awaiting the formal request for the lending project, the project design will focus on identifying states with high potential for carbon sequestration, estimating the costs associated with achieving NDC targets, and projecting the potential benefit under various growth scenarios. The second project aims to enhance landscape management and provide benefits to forest-dependent communities in Tripura and Nagaland. The methodology used in the grant to estimate ecosystem services values will be applied during project implementation in selected landscapes.
-
Targeted Technical Assistance - Maldives

The primary development objective of the GPS grant is to advance the use of knowledge-driven mechanisms to facilitate green, resilient, and inclusive development and recovery in the Maldives. While the analysis for incorporating a roadmap for natural capital accounts was finalize and integrated into the country environmental analysis (CEA) during the previous fiscal year, the CEA was officially launched and made publicly available in February 2024. This CEA has, in turn, played a pivotal role in shaping the Maldives Country Partnership Framework for FY2023–27, as well as its CCDR.
The grant activities have influenced the development of one lending project in FY24. The GPS-sponsored options analysis for revenue mobilization to enhance the sustainability and resilience of the blue economy has informed the design of a conservation trust fund—the Maldives Nature Fund—which will be established under the project. Moreover, assessments and recommendations for the sustainable use of fisheries resources have guided the implementation of the Transforming Fisheries Sector Management in South-West Indian Ocean Region and Maldives project.
Throughout the implementation of the analytical activities, the GPS task team has collaborated closely with various partners and stakeholders, particularly during consultation workshops and the launch of the CEA. A milestone workshop on Innovative Finance for Nature and Climate Action included participation and presentations from a diverse range of partners.
-
Targeted Technical Assistance - Tunisia

Tunisia’s GPS grant aims to guide the development of the tourism sector in a way that is more sustainable and resilient to threats such as climate change. It will do so by developing and using a select set of ecosystem natural capital accounts at national and subnational/local levels, along with key information related to tourism activity, to provide the Tunisian government with a decision tool. As context, there is substantial potential for ecotourism and nature-based tourism offering diversification aligned with the Tunisia 2035 Sustainable Tourism Strategy, with the overarching goal of mitigating climate change impacts on beach tourism and transforming the Tunisian tourism model with a sustainable and inclusive approach.
Considerable headway has been made in advancing the development of the ecosystem natural capital accounts and sustainable tourism indicators/accounts in FY24. Preliminary accounts have been developed at the national level, drawing on global and national data sets. These accounts will be enriched by incorporating additional data currently being gathered at the national and regional levels. The ecosystem natural capital accounts are scheduled for publication on a geo-enabled platform by the close of 2024, while the sustainable tourism indicators will be integrated into the ecosystem natural capital and sustainable tourism account compendium, expected to be available by the end of 2024. Moreover, to support the Tunisia CCDR, a study was conducted to model and evaluate ecosystem services associated with landscape management. This analytical endeavor involved creating thematic reports on critical ecosystem services such as sediment retention, surface water, underground water, carbon sequestration, and crop production. An economic assessment of these ecosystem services was carried out, culminating in a synthesis report that summarizes the core insights from the thematic reports and economic assessment. This synthesis report offers recommendations to strengthen integrated landscape management in Tunisia, including promoting nature-based solutions like afforestation, reforestation, soil and water conservation techniques, and agroforestry practices. The synthesis report will be published as a technical paper as part of the Maghreb Technical Notes Series.
Several public sector entities participated in GPS training, which took the form of a capacity building workshop on ecosystem natural capital accounting and a national training workshop for the validation of the sustainable tourism indicators’ development kit. These entities include the Ministry of Environment, Ministry of Tourism and Craft, Ministry of Economy and Planning, Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Agriculture, Water Resources and Fisheries, Ministry of Equipment and Housing, Tunisian National Tourism Office Tunisian Hotel Federation, Tourist Land Agency, National Environmental Protection Agency, Coastal Protection and Development Agency, National Institute of Statistics, National Statistics Council, and nongovernmental organizations.
-
Targeted Technical Assistance - Uzbekistan

The objective of the GPS-sponsored grant in Uzbekistan is to chart a long-term path towards climate change mitigation and environmental sustainability, while facilitating the ongoing economic transformation of the country. In FY24,
the grant focused on supporting the next green recovery Development Policy Operations by identifying areas for prior approved actions related to stronger environmental policy and the new Environmental Code. To achieve this, the grant provided just-in-time technical assistance to the government of Uzbekistan in drafting the revised law on environmental impact assessments. This assistance aimed to align the country’s environmental regulations with international good practices and the principles of the Aarhus Convention. The legal amendments included new standards for public disclosure and consultations, streamlining of the environmental assessment processes, clarification of roles and responsibilities, and the inclusion of climate change risks and mitigation requirements. The revised law elevated climate change to a cross cutting issue that is addressed upstream as part of the Strategic Environmental Assessments for government policies, plans, and programs. This ensures that climate change considerations are integrated into decision-making processes at all levels. The law also introduced the requirement for estimating greenhouse gas emissions and sinks associated with projects, emphasizing the importance of climate change mitigation. Enhanced environmental impact assessment procedures can significantly aid in embedding natural resources into decision-making processes by ensuring that the potential environmental effects of proposed projects are thoroughly analyzed and understood. This comprehensive analysis helps policy makers and stakeholders to make informed decisions about the design, sequencing, and appropriateness of projects, ensuring that natural resources are considered and protected. Engaging a range of key stakeholders and building capacity for environmental analysis can further integrate these considerations into policy processes, promoting sustainable development.
The GPS grant activities provided foundational elements for the Uzbekistan Second Inclusive and Resilient Market Economy Development Policy Operation. Specifically, it informed Pillar 3, which is focused on social inclusion and green resilience with the aim of supporting reforms to increase green resilience, strengthen social protection, and support vulnerable groups in Uzbekistan. Among other reforms, the Development Policy Operation listed strengthening the regulatory frameworks for air quality management and for environmental impact assessment under Prior Action 10.
The Center of the Ecological Expertise of the Ministry of Ecology, Environmental Protection and Climate Change led the effort, with the grant team being part of a working group responsible for drafting the new draft environmental impact assessment law. This working group included other key agencies such as the Environmental Law Institute, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, OSCE, and NBT Consulting, ensuring a collaborative and inclusive approach. In terms of capacity building and institutionalization, a two-day workshop was held on December 5–6, 2023, to help align Uzbekistan’s environmental impact assessment law with international standards. Participants were from the working group, with female participants making up about 35 percent of the group.

