Indonesia stands as a significant economic player both globally and within the East Asia and Pacific region. As the world's fourth most populous country, Indonesia boasts a diverse and dynamic economy that has demonstrated resilience and growth over the past decades.
In terms of the Human Capital Index, Indonesia has made noteworthy progress, reflecting its ambitious efforts to enhance health and education outcomes. Such improvements are critical as Indonesia continues to strive for greater economic competitiveness and become a high-income country by 2045. Efforts to build stronger health systems, improve nutrition, and reduce stunting are at the forefront of government actions.
Indonesia’s Health Priorities
Indonesia has been focusing on improving the health of its citizens, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Despite its large population of 270 million and diverse geography, Indonesia was one of the first countries to administer 100 million doses of COVID-19 vaccines. After the pandemic, the country continues to strengthen its health sector, focusing on primary care, referral care, health system resilience, and digital health initiatives.
The pandemic shed light on the urgent need to strengthen the country’s health system to better prepare for and respond to any future health emergencies. In response, the Ministry of Health (MoH) launched the Health System Transformation Agenda (HSTA) in 2022. This agenda built on six pillars: primary health care, referral care, health resilience, human resources, health financing, and technology.
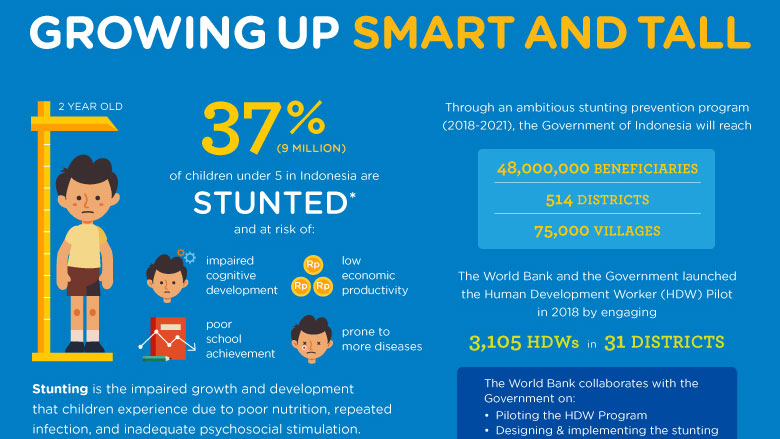
Another key focus is enhancing nutrition and reducing stunting among children which has been a persistent challenge in Indonesia. Recognizing the long-term implications of stunting on cognitive development, economic productivity, and overall quality of life, the government has rolled out comprehensive strategies such as the National Strategy to Accelerate Stunting Prevention which has allocated significant resources for coordinated action across ministries to tackle the underlying factors of stunting.